AML automation software has revolutionized the financial industry, offering a powerful solution to the complex challenges of anti-money laundering (AML) compliance. This technology empowers financial institutions to detect and prevent financial crime with greater efficiency, accuracy, and speed, transforming how they manage risk and protect their reputation.
AML automation software leverages advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to analyze vast amounts of data, identify suspicious transactions, and automate critical processes like customer due diligence (CDD) and risk assessments. This allows institutions to stay ahead of evolving threats and comply with stringent regulations while optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs.
AML Automation Software: Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of financial services, the importance of robust Anti-Money Laundering (AML) compliance has become paramount. As financial institutions grapple with increasingly sophisticated financial crimes, traditional manual AML processes are proving inadequate. Enter AML automation software, a game-changer that leverages technology to streamline and enhance AML compliance efforts, ensuring both effectiveness and efficiency.
Importance of AML Automation Software
AML automation software plays a crucial role in the financial industry by automating various tasks related to AML compliance. It empowers institutions to identify, assess, and mitigate money laundering risks more effectively. This is achieved through the use of advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML), enabling software to analyze vast amounts of data and identify suspicious patterns that may otherwise go unnoticed.
Key Challenges Addressed by AML Automation Software
AML automation software addresses a multitude of challenges faced by financial institutions in their fight against money laundering. Some key challenges include:
- Manual Processes and Human Error: Traditional AML processes often involve manual data analysis and review, which are time-consuming and prone to human error. Automation helps streamline these processes, reducing errors and improving efficiency.
- Growing Volume of Data: Financial institutions are constantly dealing with increasing volumes of data, making it difficult to manually analyze and identify suspicious activities. AML automation software can handle massive datasets and identify patterns that might be missed by human analysts.
- Evolving Money Laundering Techniques: Money launderers are constantly evolving their techniques to evade detection. AML automation software can adapt to these changes by leveraging AI and ML to identify new patterns and trends.
- Regulatory Compliance: AML regulations are constantly evolving, making it challenging for financial institutions to stay compliant. AML automation software can help institutions keep up with these changes and ensure ongoing compliance.
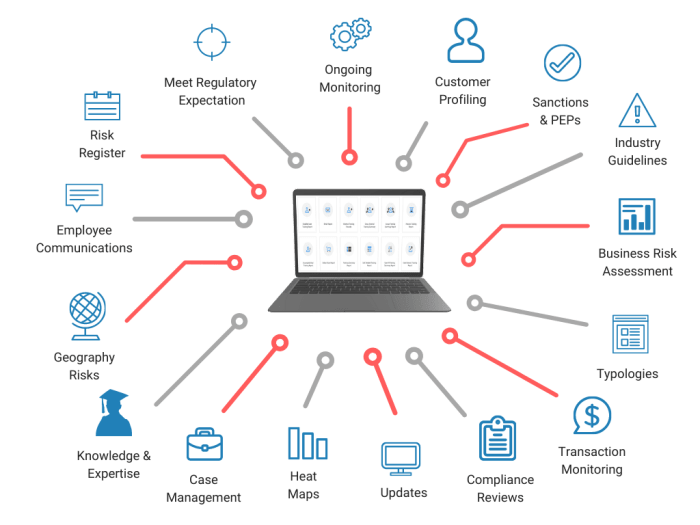
Features and Functionalities of AML Automation Software
Typical AML automation software encompasses a wide range of features and functionalities, designed to address various aspects of AML compliance. Some common features include:
- Transaction Monitoring: Real-time monitoring of transactions to identify suspicious activity based on pre-defined rules and patterns.
- Customer Due Diligence (CDD): Automated verification of customer identities and background checks to ensure compliance with KYC (Know Your Customer) regulations.
- Risk Assessment: Automated assessment of customer and transaction risk profiles based on predefined criteria and historical data.
- Alert Management: Automated generation and management of alerts for suspicious activities, facilitating timely investigations and reporting.
- Case Management: Automated tracking and management of AML investigations, including documentation and reporting.
- Reporting and Analytics: Generation of comprehensive reports and dashboards for monitoring AML performance, identifying trends, and supporting regulatory reporting.
Key Components of AML Automation Software
AML automation software comprises several core components that work together to ensure effective AML compliance. These components are designed to address specific aspects of AML risk management and compliance.
Transaction Monitoring
Transaction monitoring is a critical component of AML automation software. It involves analyzing financial transactions in real-time to identify suspicious activity. This process typically involves:
- Rule-based Monitoring: Defining specific rules and thresholds to flag transactions that deviate from expected patterns.
- Pattern Recognition: Using AI and ML algorithms to identify complex patterns and anomalies in transaction data.
- Behavioral Analysis: Analyzing customer behavior and transaction history to identify unusual or suspicious activity.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
CDD is another crucial component of AML automation software. It involves verifying the identities of customers and conducting background checks to assess their risk profile. This process typically includes:
- Identity Verification: Verifying customer identities using various data sources, including government databases and credit bureaus.
- Sanctions Screening: Checking customer names and addresses against international sanctions lists to ensure they are not associated with individuals or entities subject to sanctions.
- PEP (Politically Exposed Person) Screening: Identifying individuals who hold prominent public positions, as they may pose a higher risk of money laundering.
- Adverse Media Screening: Searching for negative news or information about customers that may indicate potential money laundering risks.
Risk Assessment
Risk assessment is an essential component of AML automation software, allowing institutions to prioritize their AML efforts based on the level of risk associated with individual customers and transactions. This process typically involves:
- Customer Risk Profiling: Assigning risk scores to customers based on factors such as their business activities, geographic location, and financial history.
- Transaction Risk Scoring: Assigning risk scores to individual transactions based on factors such as the amount, currency, and destination.
- Risk Mitigation Strategies: Developing and implementing appropriate risk mitigation strategies for high-risk customers and transactions.
Role of AI and ML in AML Automation
AI and ML are playing an increasingly important role in AML automation, enabling software to analyze vast amounts of data, identify complex patterns, and make more accurate predictions. Some key applications of AI and ML in AML automation include:
- Enhanced Transaction Monitoring: AI and ML algorithms can identify complex patterns and anomalies in transaction data that may be missed by traditional rule-based systems.
- Automated Customer Due Diligence: AI and ML can automate various aspects of CDD, such as identity verification and sanctions screening.
- Real-time Risk Assessment: AI and ML can continuously assess risk profiles based on real-time data, enabling more proactive risk management.
- Fraud Detection: AI and ML algorithms can identify and predict fraudulent activity based on patterns and anomalies in transaction data.
Integration with Other Systems
Integrating AML automation software with other systems, such as CRM (Customer Relationship Management) platforms and banking platforms, can significantly enhance its effectiveness. This integration allows for seamless data sharing and analysis, improving the overall AML compliance process. Some key benefits of integration include:
- Centralized Data Access: Integrating AML automation software with other systems provides a centralized view of customer and transaction data, facilitating more comprehensive risk assessments.
- Automated Workflow: Integration can automate various AML workflows, reducing manual intervention and improving efficiency.
- Real-time Risk Monitoring: Integrating with banking platforms allows for real-time monitoring of transactions, enabling faster detection and response to suspicious activity.
- Improved Customer Experience: Integration can streamline customer onboarding and verification processes, improving the overall customer experience.
Implementing AML Automation Software
Implementing AML automation software within an organization requires a well-defined plan and careful consideration of various factors. This process involves several key steps to ensure successful adoption and maximize the benefits of the software.
Steps Involved in Implementation
- Needs Assessment: Identify the specific AML compliance challenges and requirements of the organization to determine the most appropriate software solution.
- Software Selection: Evaluate different AML automation software solutions based on features, functionality, pricing, and compatibility with existing systems.
- Data Integration: Integrate the AML automation software with existing systems, such as CRM platforms and banking platforms, to ensure seamless data flow and analysis.
- Configuration and Customization: Configure the software to meet the specific AML compliance requirements of the organization, including defining rules, thresholds, and risk profiles.
- User Training: Provide comprehensive training to users on how to effectively use the software, interpret results, and manage alerts.
- Testing and Validation: Conduct thorough testing and validation of the software to ensure its accuracy and effectiveness in identifying suspicious activities.
- Deployment and Monitoring: Deploy the software and continuously monitor its performance, making adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness.
Challenges and Considerations During Implementation
Implementing AML automation software can present several challenges and considerations, which need to be addressed carefully to ensure a successful implementation.
- Data Integration: Integrating the software with existing systems can be complex, requiring careful planning and coordination to ensure data accuracy and consistency.
- Training and User Adoption: Training users on how to effectively use the software is crucial for successful adoption. Resistance to change and lack of understanding can hinder the implementation process.
- Cost and Resource Allocation: Implementing AML automation software can involve significant upfront costs and ongoing resource allocation for maintenance and support.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the chosen software solution meets all relevant regulatory requirements and industry standards.
- Ongoing Maintenance and Updates: AML automation software requires ongoing maintenance and updates to keep pace with evolving regulatory requirements and money laundering techniques.
Best Practices for Successful Implementation
Following best practices can significantly enhance the chances of a successful implementation of AML automation software. Some key best practices include:
- Clearly Define Objectives: Establish clear objectives for implementing AML automation software, including specific goals for improving AML compliance and reducing risk.
- Involve Stakeholders: Involve key stakeholders from different departments, including compliance, IT, and operations, in the implementation process to ensure buy-in and collaboration.
- Phased Rollout: Implement the software in phases, starting with a pilot program to test its effectiveness and address any issues before full deployment.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Regularly monitor the software’s performance and identify areas for improvement, making adjustments as needed to optimize its effectiveness.
Benefits of AML Automation Software
Implementing AML automation software offers numerous benefits for financial institutions, enabling them to enhance their AML compliance programs, mitigate risks, and improve operational efficiency.
Key Benefits
- Increased Efficiency: Automating AML tasks frees up valuable time and resources for compliance professionals, allowing them to focus on more strategic initiatives.
- Reduced Costs: By automating manual processes, aml automation software can significantly reduce operational costs associated with AML compliance.
- Improved Accuracy: Automated systems are less prone to human error, leading to more accurate identification and assessment of AML risks.
- Enhanced Compliance: AML automation software helps institutions stay up-to-date with evolving regulations and industry standards, ensuring ongoing compliance.
- Proactive Risk Management: Real-time monitoring and risk assessment capabilities enable institutions to proactively identify and mitigate potential AML risks.
- Improved Customer Experience: Streamlined customer onboarding and verification processes can improve the overall customer experience.
Examples of Risk Mitigation
AML automation software can help organizations mitigate various AML risks, including:
- Customer Onboarding Risk: Automated identity verification and background checks help mitigate the risk of onboarding customers associated with money laundering activities.
- Transaction Risk: Real-time transaction monitoring and risk assessment help identify and prevent suspicious transactions related to money laundering.
- Sanctions Risk: Automated sanctions screening helps ensure that institutions are not doing business with individuals or entities subject to sanctions.
- Reputational Risk: Effective AML compliance helps protect an institution’s reputation by reducing the risk of being involved in money laundering activities.
Real-World Case Studies
Numerous real-world case studies demonstrate the positive impact of AML automation software on businesses. For example, a large financial institution implemented AML automation software to streamline its customer due diligence process. The software automated identity verification, sanctions screening, and PEP checks, significantly reducing the time and effort required for customer onboarding. This resulted in improved efficiency, reduced costs, and enhanced compliance.
Future Trends in AML Automation
The field of AML automation is constantly evolving, with new technologies and regulatory changes shaping the future of AML compliance. Understanding these trends is crucial for organizations to stay ahead of the curve and ensure their AML programs remain effective and efficient.
Emerging Trends
- Blockchain Technology: Blockchain technology offers potential for enhanced transparency and traceability of transactions, making it more difficult for money launderers to obscure their activities. AML automation software is incorporating blockchain features to improve transaction monitoring and risk assessment.
- Advanced Analytics: The use of advanced analytics techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, is expanding in AML automation. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data to identify complex patterns and anomalies, improving the accuracy and effectiveness of AML detection.
- Regulatory Changes: Regulatory bodies are constantly evolving AML regulations to keep pace with evolving money laundering techniques. AML automation software needs to be adaptable to these changes, ensuring ongoing compliance and effectiveness.
Impact on the Future of AML Automation
These emerging trends are expected to have a significant impact on the future of AML automation software. As technologies advance and regulations evolve, AML automation software will become more sophisticated, offering more robust capabilities for identifying and mitigating money laundering risks. This will lead to more effective AML compliance, improved risk management, and reduced costs for financial institutions.
Preparing for Future Trends
Organizations can prepare for these future trends by:
- Staying Informed: Keep abreast of the latest advancements in AML automation technology and regulatory changes. Attend industry conferences, read industry publications, and network with experts in the field.
- Investing in Technology: Invest in AML automation software that leverages advanced technologies, such as blockchain and AI, to enhance compliance capabilities.
- Developing Adaptable Strategies: Develop flexible and adaptable AML compliance strategies that can readily accommodate evolving technologies and regulations.
Comparison of Leading AML Automation Software
The market offers a wide range of AML automation software solutions, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Selecting the right software for an organization depends on its specific needs, budget, and compliance requirements. This table provides a comparison of some popular AML automation software solutions based on key features, pricing, and target audience.
| Software Name | Key Features | Pricing | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software A | Transaction monitoring, customer due diligence, risk assessment, reporting and analytics, AI-powered fraud detection | Subscription-based pricing, starting at $X per month | Financial institutions of all sizes, including banks, credit unions, and insurance companies |
| Software B | Customer due diligence, sanctions screening, PEP screening, adverse media screening, case management | Per-user pricing, starting at $Y per user per month | Mid-sized and large financial institutions with complex AML compliance needs |
| Software C | Transaction monitoring, risk assessment, alert management, reporting and analytics, integration with CRM platforms | Flat fee pricing, starting at $Z per year | Small and medium-sized financial institutions with basic AML compliance requirements |
Pros and Cons of Each Software Solution
Each AML automation software solution has its own pros and cons, which should be carefully considered during the selection process. For example, Software A may offer a wider range of features and functionality but may be more expensive than Software C. Software B may be more suitable for larger institutions with complex AML compliance needs, while Software C may be a better fit for smaller institutions with more basic requirements.
Insights into the Selection Process
When selecting AML automation software, organizations should consider the following factors:
- Specific AML Compliance Needs: Identify the specific AML compliance challenges and requirements of the organization.
- Budget: Determine the budget allocated for AML automation software and select a solution that fits within the budget constraints.
- Features and Functionality: Evaluate the features and functionality of different software solutions to ensure they meet the organization’s needs.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Ensure that the software can be seamlessly integrated with existing systems, such as CRM platforms and banking platforms.
- User Friendliness: Choose a software solution that is easy to use and understand for all users.
- Customer Support: Select a vendor that provides excellent customer support and technical assistance.






